High CPU Usage by audiodg.exe: SOLVED in Windows 10/11
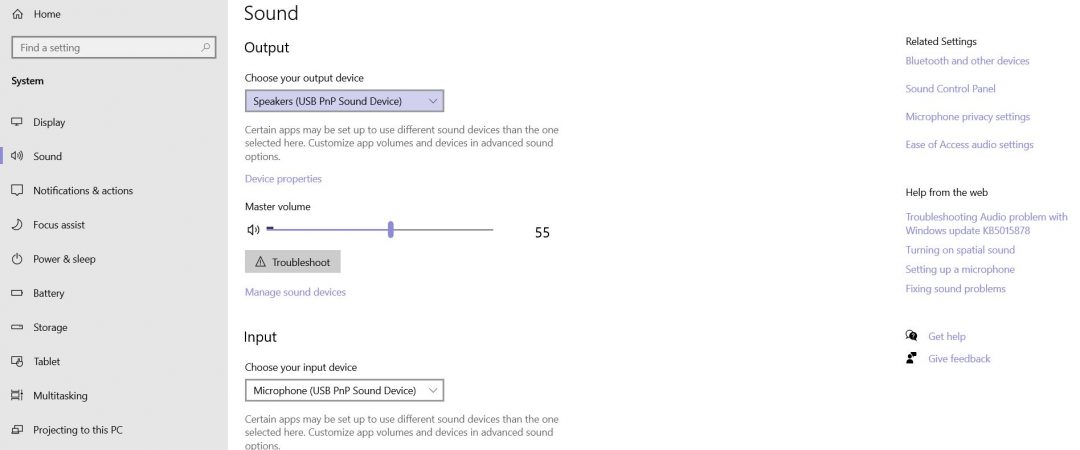
What’s audiodg.exe?
AudioDg.exe is one of those processes that are often left running on your PC. This program is responsible for playing sounds such as music, alarms, alerts, etc. However, it does so quietly, without interfering with other applications. If you don’t pay attention to what is happening on your computer, you might never notice that audiodg.exe is running. But once you do realize that there is something wrong, stopping it becomes essential.
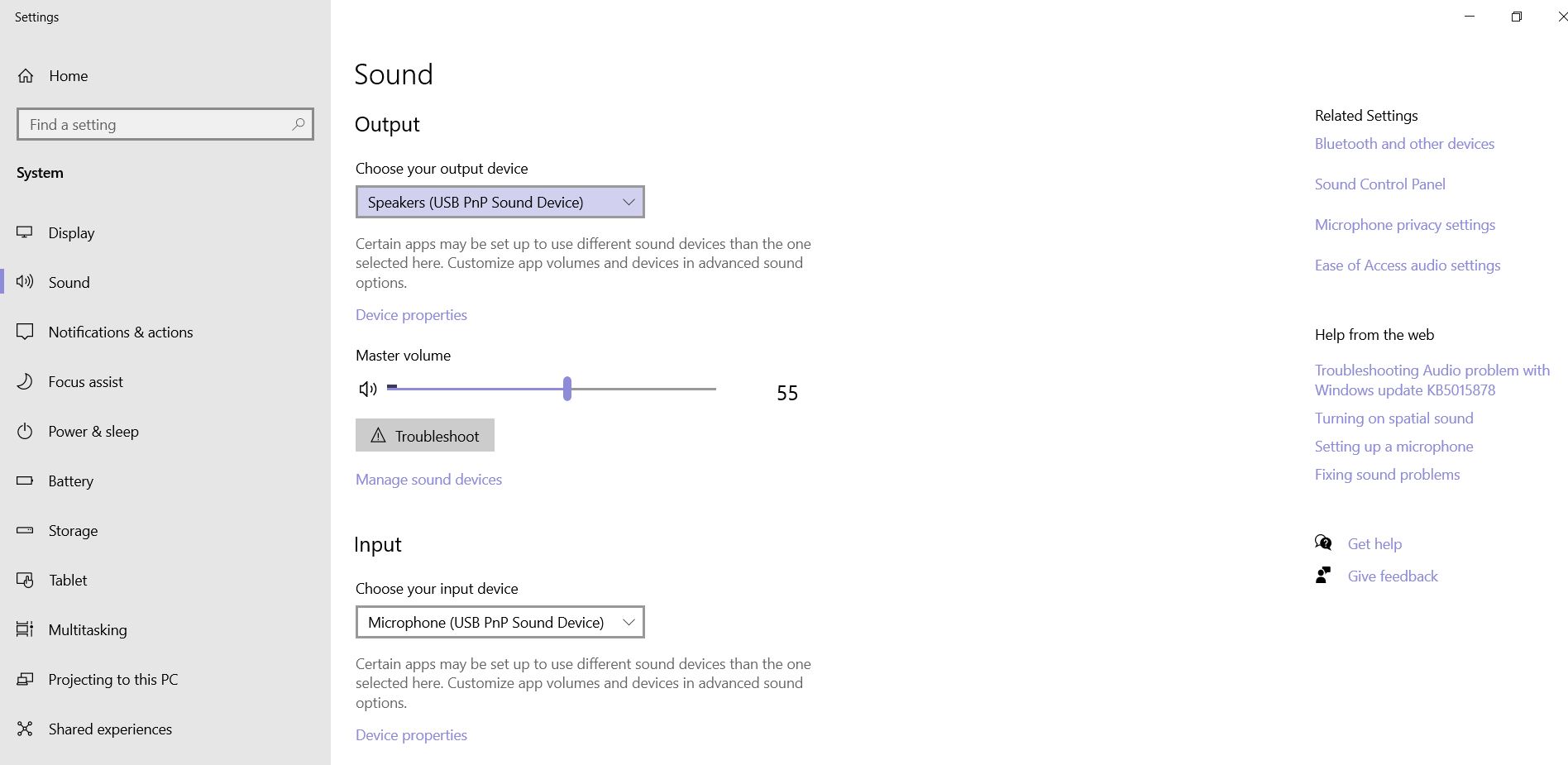
What makes audiodg.exe use a lot of CPU?
Audiodg.exe is one of those processes you never really think about because it doesn’t seem like much of a problem. However, there are times where it can actually become a big problem. If you’re experiencing high CPU usage while running audiodg.exe, here are some things to check out.
1. Check Your Audio Drivers
If you’ve been having issues with audiodg.exe hogging up your computer’s CPU, chances are good that your audio drivers are outdated. You’ll want to make sure that you update your sound card drivers regularly. This is especially true if you use multiple devices such as headphones, speakers, and microphones.
2. Update Your Antivirus Software
Another reason why audiodg.exe could be causing you trouble is because your antivirus software isn’t keeping up with current threats. Make sure that you keep your anti-malware program updated. In addition, you should disable any third party programs that aren’t necessary. For example, if you don’t use a VPN, you shouldn’t have anything installed that requires access to the internet.
3. Disable Third Party Programs
You might find that disabling certain programs helps reduce the amount of CPU cycles consumed by audiodg.exe. For example, if your browser uses Adobe Flash Player, you can disable it. Another option is to turn off automatic updates for your operating system. These options won’t stop malware from being downloaded onto your machine, but they will help prevent audiodg.exe from consuming too many resources.
Audiodg.exe takes up a lot of CPU time.
The Windows Audio Device Driver (audiodg.exe) causes high CPU usage when certain audio effects are enabled such as Dolby Atmos, DTS:X, or 7.1 Surround Sound. This issue occurs because the driver uses DirectSound APIs to play sound files. If you experience high CPU usage while playing media, try disabling some of the following options:
• Enable Dolby Atmos, enable DTS:X, and/or enable 7.1 surround sound.
• Change the audio sample rate to 48 kHz.
• Update the device driver.
If none of those work, contact Microsoft Customer Support.
How To Fix High CPU Use By audiodg.exe?
If you are experiencing high CPU usage while playing audio files, it could be due to one of many reasons. Here we list down some possible causes and solutions to fix audiodg.exe high CPU usage issue.
1. Windows 10 Audio Driver Issues
Windows 10 uses the Realtek ALC1150 codec, which is known to cause issues with certain hardware configurations. If you are facing problems with audio playback, try uninstalling the driver and installing the latest version from Microsoft. You can download the latest version here.
2. Hardware Problems
Sometimes, there might be a problem with your hardware components such as speakers, microphone, etc. In case you are having trouble with your audio device, check whether everything is plugged properly. Also make sure that the volume levels are set correctly.
3. Software Issues
If none of the above fixes work, try disabling all the bells and whistles in your sound settings. This includes things like equalizer, effects, etc.
Solution 1: Slow down the sample rate.
The sampling rate refers to how many times per second you are capturing sound. A lower sampling rate means less data is being captured, resulting in smaller files. This can make it easier to store large amounts of audio on mobile devices.
“Use compression”
Compression reduces the amount of data needed to represent a given signal. Compressing audio files makes them smaller and allows you to save them to disk. You can use software like Audacity to compress audio files.
Use fewer channels
If you’re recording stereo music, try reducing the number of channels from stereo to mono. Mono recordings take up much less space than stereo ones.
Solution 3: Change the sound card’s driver
To update drivers, go to Device Manager and uncheck the old one. Then install the new driver. Before you do it, uninstall the old one. You can download the latest version of the drivers from the manufacturer’s website or use Driver Easy.
Solution 4: Disable volume adjustment
Rightclick on your speaker icon, select “Properties”, uncheck the box next to “Adjust volume automatically”. This way you won’t have to adjust it manually everytime you want to listen to music.
Solution 5: Update your game or software that you care about
The problem: You are running a web application based on PHP/MySQL. You want to make sure that you keep it up to date. But how do you know what version of PHP/MySQL you are actually running? How do you check whether there are security issues in your code? And how do you find out about changes in the database schema?
Solution: Use phpinfo()
phpinfo() displays information about your installed PHP extensions and configuration settings. This includes everything from the operating system PHP is running on, to the MySQL extension used, to the version of PHP itself.
In addition, phpinfo() provides detailed information about the current state of your server environment. For example, it tells you where your files are located, what modules are loaded, and even lists the contents of your memory.
If you run into problems while updating your software, use phpinfo() to identify the cause.
Solution 6: Update the driver for your sound card and any other hardware that makes sounds.
If you are experiencing problems with audio output while playing games, it could be because the drivers installed on your system are outdated. To fix this problem, we recommend downloading the latest versions of the drivers from Intel’s download center. The solution for Linux Mint 17.x 32-bit is similar to the one above, except that you must use the package manager to install the updated drivers. For example, open up a terminal window and type the following command: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade -y && sudo apt autoremove -y && sudo reboot
To check whether the latest drivers are already installed, run the following command: lspci | grep VGA If there is no output,

Tim Wiley was a tech writer for seven years at Recode. In that time, he covered everything from basic browser.js and URL parameters to XHRs, performance, malware, security, enterprise apps, social media, and Windows secrets. He also written about how to hack Signal in 2016 and how to resist, or possibly even conquer, the zero-day threat.