What are Temporary Files and is it Safe to Delete them?
What Exactly Are Temporary Files?
Temporary files are used by your computer to store information while programs run. These files are usually deleted automatically once the program finishes running. However, there are times when you want to keep certain files around temporarily. For example, you might use a web browser to download a file from a website. If you close the browser without saving it, the temporary file will disappear. In addition, some programs require temporary files to function properly.
If you’re having trouble deleting temporary files manually, try one of the following methods:
1. Delete All Temp Files Automatically
You can set Windows 10 to delete all temporary files every night. Then, under “Backup Options,” select “Delete old backup files.” This method works well for most people, but it won’t work if you’ve disabled automatic backups.
2. Use a Cleaner
There are several free tools that help you clear temporary files. One popular option is CCleaner. You can find instructions here. Another option is BleachBit. Instructions for both tools can be found here.
3. Manually Delete Files
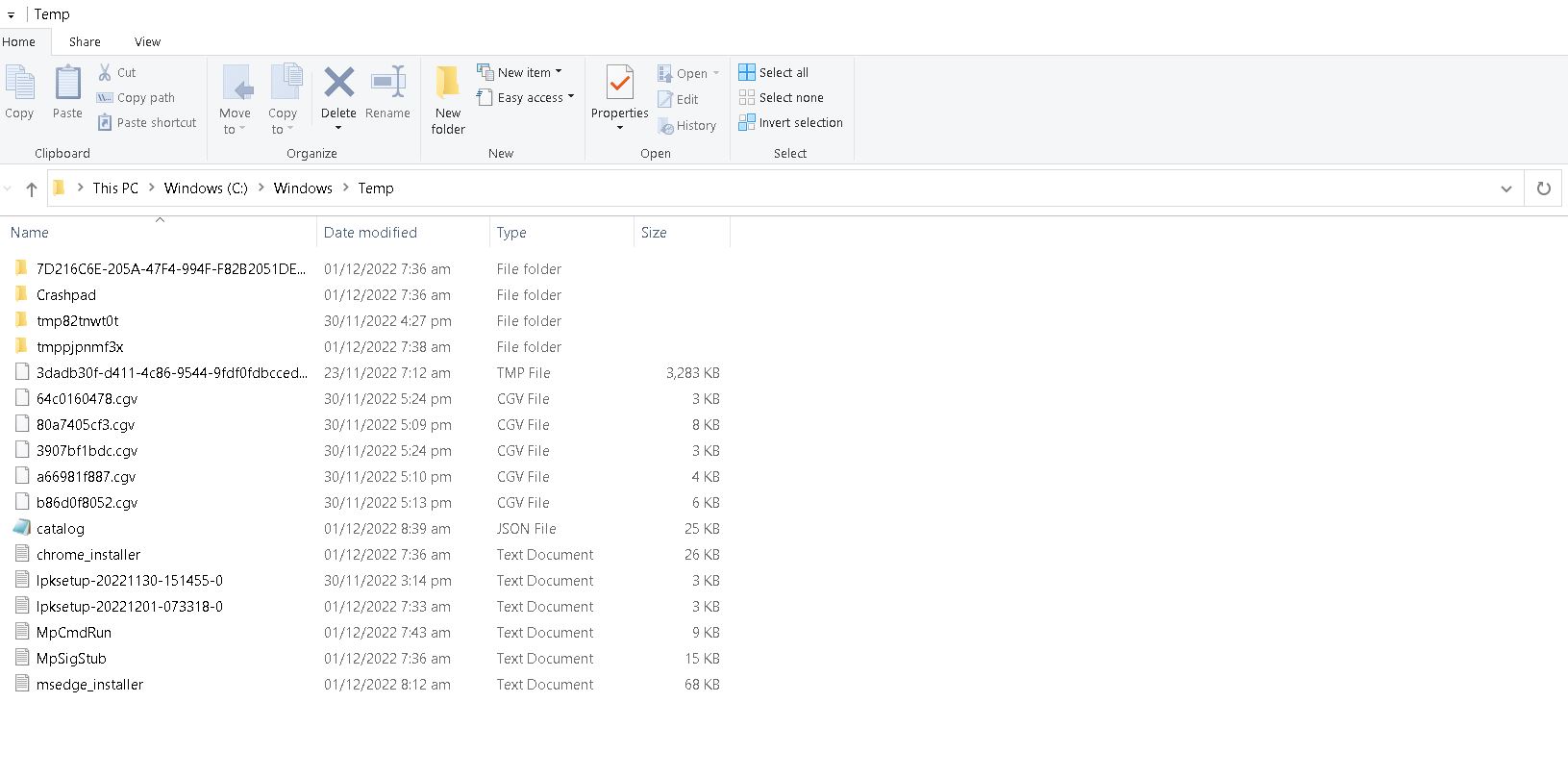
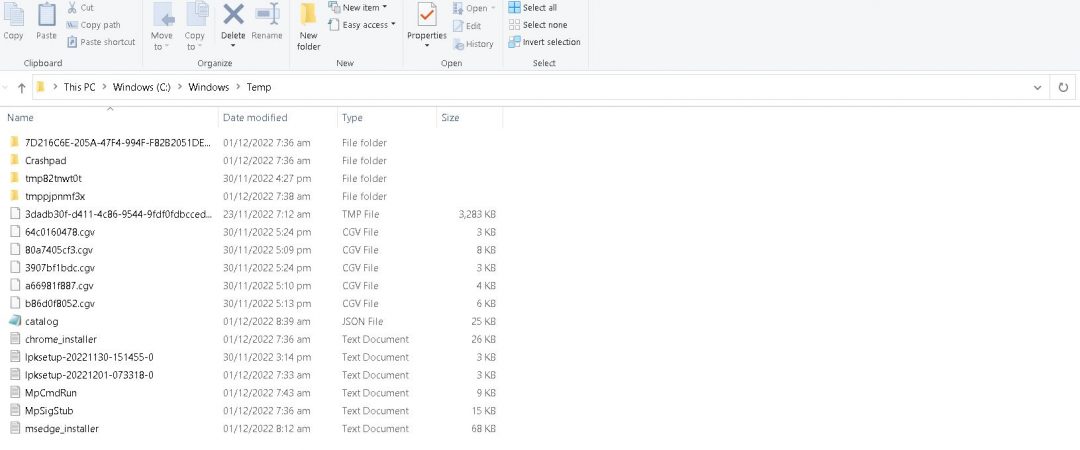
Location of Temporary Files
Temporary files are used to store temporary data while programs run. These files are usually located in the same folder where the operating system stores the system files. You can use the command prompt to view the location of temp files. To do this, type the following command into the command prompt window:
This command lists the contents of the directory specified by the path argument. In this case, it displays the names of the folders and subfolders within the current working directory. If there are no items listed, the command does nothing.
The /a option specifies that the command display the full name of each file and folder. The /b option specifies that the command list hidden files and directories. The /c option specifies that the command include the extension of each item displayed. For example, if you specify the /c option, the command displays the filename followed by the extension.
You can change the location of temporary files by changing the values of the environment variables named TMP and TEMP. By default, both variables contain the same value, which is the folder containing the system files. However, you can set different values for these variables. This allows you to move the temporary files to another location.
To see how the TMP and TEMP variables work, open Notepad and enter the following text:
TMPC:\Temp\tempfile1
What is the purpose of the temporary files on my computer?
Temporary files are essential for everyday use of a computer. Without them, you wouldn’t be able to open a file, save it, edit it, print it, or even close it without losing work. But what happens when temporary files take over your entire hard drive? And why do some people have hundreds of gigabytes worth of them?
The most common reason for having large amounts of temporary files on your PC is because you’re downloading software, music, movies, games, etc., and saving those downloads to your hard drive. If you’ve ever downloaded anything from the internet, you know how long it takes to download a single file. When you start downloading multiple files at once, things can really slow down. This is where temporary files come into play.
When you download a program or game, it usually creates a folder called “Downloads.” Inside that folder, it saves every piece of information about the program or game you just downloaded. For example, if you download a video game, it might store the name of the game, the version number, the size of the file, and even the date you downloaded it. All of this data gets saved inside a folder named “Downloads,” and that folder itself gets saved somewhere else on your hard drive. Once you finish downloading everything, you’ll see a lot of empty folders on your desktop. These are the places where your temporary files live.
If you have a lot of temporary files on your hard drive, it could indicate that you’re downloading a lot of stuff. If you want to free up space on your hard drive, try deleting unused programs and cleaning out old files. Also, make sure you’re not downloading copyrighted material.
When Should You Remove Temporary Files From Your Computer?
Temporary files are those files that are automatically generated while you’re working on a project. They might include things like cache files, cookies, images, videos, documents, and even browser history. While there aren’t any hardand-faste…
The best way to make sure you’re getting the most out of your web hosting package is to use our free tools. We’ve put together some useful resources to help you monitor your site traffic, find out what’s happening behind the scenes, and ensure that everything is running smoothly.
If you want to know how many visitors are coming to your site, where they’re coming from, and how long they spend on each page, we’ve got you covered. You’ll learn how to track visits, analyze data, and see exactly what people are doing on your site.
We’ve also included information on how to optimize your site for mobile devices, including tips on responsive design and creating a mobile version of your site. If you want to know how your site looks on different browsers, check out our Browser Support section.
Is deleting temporary files safe?
Temporary files are used by programs like browsers, email clients, and web servers to store information about how you use the program. They’re usually deleted automatically once the program closes, but sometimes it’s necessary to delete them manually. If you do decide to delete them, make sure you know what you’re doing.
There are many different types of temporary files, including browser cache files, cookies, and indexing files. Some of them aren’t even stored on your computer; they’re just kept online. These include things like your browsing history, saved passwords, and bookmarks.
The most common type of temporary file is the cache file. This contains information about the way you’ve been using your browser. For example, it might contain information about where you went on the internet recently, or whether you visited certain sites. When you close down your browser, the cache file gets deleted. But there are other kinds of temporary files too.
If you want to delete one, you’ll need to find out what it is. Here, you’ll find a list of all the temporary files that are being held locally.
You can also look up each individual file on Microsoft’s support site. Just enter the name into the search box.
Once you’ve found the file you want to delete, open it up in Notepad or another text editor. Look for something like “C:\Users\\AppData\Local\Temp\” or “\temp\.” In some cases, you’ll need to change to your username. Then, simply delete the file.
Why Should You Delete Temporary Files?
Temporary files are used to store information while you’re working on something else. They’re usually located in folders like Temp or My Documents. While it’s easy enough to delete them manually, there are some reasons why you might want to do it automatically. Here are five things you should know about deleting temporary files.
1. Temporarily storing data
When you open a file, you’ll often see a small icon next to it called “Open With.” This lets you choose what program opens the document. If you don’t use that particular application every day, you probably just ignore it. But if you’re trying to save space on your hard drive, you might want to consider changing your default settings.
2. Unused software
If you’ve downloaded a piece of software, you might still have access to the trial version. When you close down the program, though, it doesn’t go away completely. Instead, it leaves behind a bunch of temporary files. These files contain information about how the program works, including where it stores your documents. So even if you uninstall the program, you might still find yourself looking at old versions of those documents.
3. Hidden files
You can view hidden files by pressing Ctrl+H on Windows computers or Shift+Ctrl+H on Macs. By default, most operating systems hide certain types of files. For example, you might not want to show the contents of your recycle bin because it contains deleted items. However, you can change the setting to make sure you always see everything.
An Overview of How to Delete Temporary Files
Temporary files are those files that are used temporarily while working on a project. These include documents, images, videos, audio recordings, etc. They are usually deleted automatically once the project is completed. However, there are times when we might need to keep some of these files around. This could happen if we need to open the same file again later, or if we need to save our work for future reference. In such cases, we can use the Recycle Bin feature to permanently delete these files.
Windows 10 provides us with a built-in tool called the Recycling Bin. Once opened, we can see all the files and folders that have been placed into the bin. If we select one of these items, we’ll be able to see the path to the location where it has been saved. From here, we can choose to either move the item out of the bin or permanently delete it.
In case you don’t remember where the Temp folder is located, let me help you out. You can locate it under the following locations:
C:\Users\\AppData\Local\Temp
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet Files
Deleting Files Isn’t Enough: Shred Cube Is The Only Long-Term Solution
ShredCube is an easy way to securely shred confidential documents. You just plug it into your computer and let it do the work. After you’re done, there are no traces left behind.
The problem with most file shredders is that they don’t actually erase the data. They simply make it unreadable. This leaves open the possibility that someone could recover the information later.
That’s why we developed ShredCube. We took the best parts of our previous products and combined them into one tool that makes sure that every piece of paper gets shredded forever.

Tim Wiley was a tech writer for seven years at Recode. In that time, he covered everything from basic browser.js and URL parameters to XHRs, performance, malware, security, enterprise apps, social media, and Windows secrets. He also written about how to hack Signal in 2016 and how to resist, or possibly even conquer, the zero-day threat.